The Cummins diesel fuel injector is the core component in the diesel engine fuel system, responsible for injecting high-pressure fuel into the combustion chamber in the form of precise timing, amount, and atomization, which directly affects the engine’s combustion efficiency, power output, and emission level.
What does a diesel fuel injector do?
1. Fuel Atomization
Converts high-pressure fuel into extremely fine mist-like droplets through tiny spray holes, increasing the contact area with air to ensure full combustion.
2. Precision Metering
Controls the amount of fuel injected each time according to the instruction from the engine control unit (ECU), matching the demand under different working conditions (e.g., idling, acceleration, high load, etc.).
3. Timed Injection
Injects fuel strictly according to the injection timing calculated by the ECU (e.g., pre-injection, main injection, post-injection), optimizing the combustion process and reducing noise and emissions.
4. Pressure Maintenance
Maintains a stable high pressure (up to 2000 bar or more) in the common rail system to ensure the atomization effect and injection speed.
Structural Components of an Injector
Cummins injectors usually contain the following key components:
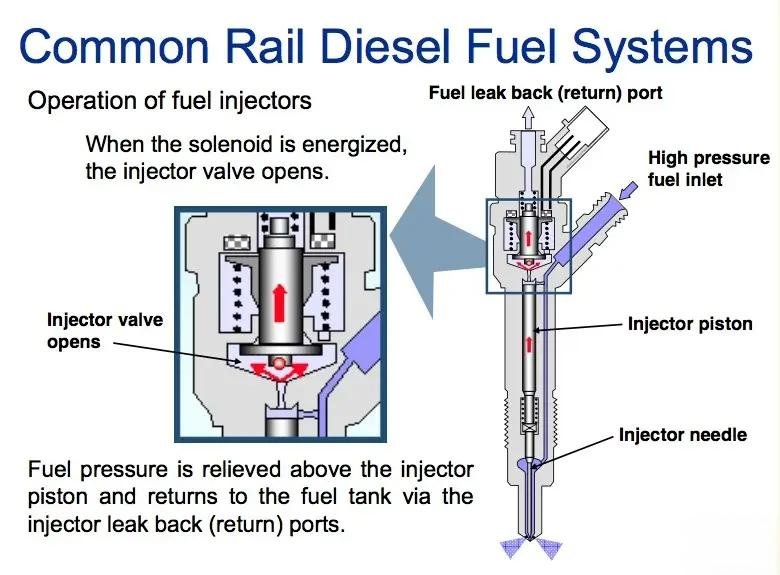
Solenoid valve/piezoelectric crystal: receives signals from the ECU to quickly turn fuel injection on/off.
Needle valve: rises under high-pressure fuel push and fuel is injected; resets and closes after pressure drops.
Spray holes: Precision-machined micro-holes (about 0.1mm in diameter), affecting the shape of atomization and penetration.
High-pressure fuel line: connected to the common rail system and subject to extreme pressure.
Return passage: Discharges leaking fuel and maintains system pressure balance.




