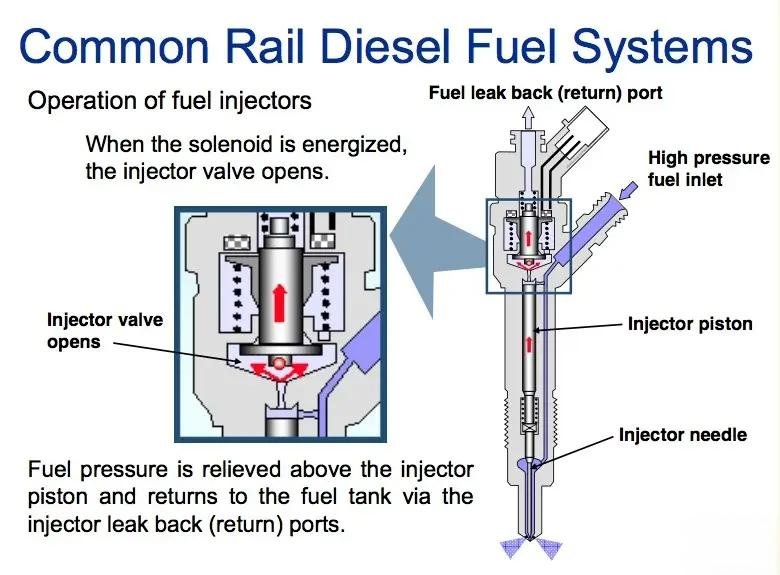
(Take an electronically controlled common rail system as an example)
- High-pressure fuel supply
The high-pressure pump pressurizes the fuel and sends it to the common rail pipe. The injector is connected to the common rail through the fuel pipe and remains in a high-pressure state, ready for injection.
2. ECU control signal
The ECU calculates the injection timing and duration according to the sensors (crankshaft position, camshaft position, load, etc.), and sends a pulse signal to the injector solenoid valve.
3. The injecting process
Opening stage: the solenoid valve is energized, the control valve opens, the high-pressure fuel pushes the needle valve up, and the injection hole opens.
Injection stage: The fuel is atomized and sprayed from the injection hole with very high pressure, and the amount of fuel injected is determined by the pulse width of the ECU.
Closing stage: the solenoid valve is de-energized, the control valve is reset, the needle valve is rapidly closed under the action of spring force, and the fuel injection is terminated.
4. Multi-stage injection
Modern Cummins engines may use multiple injections (e.g., pre-injection to reduce combustion noise, main injection to ensure power, and post-injection to reduce particulate matter).